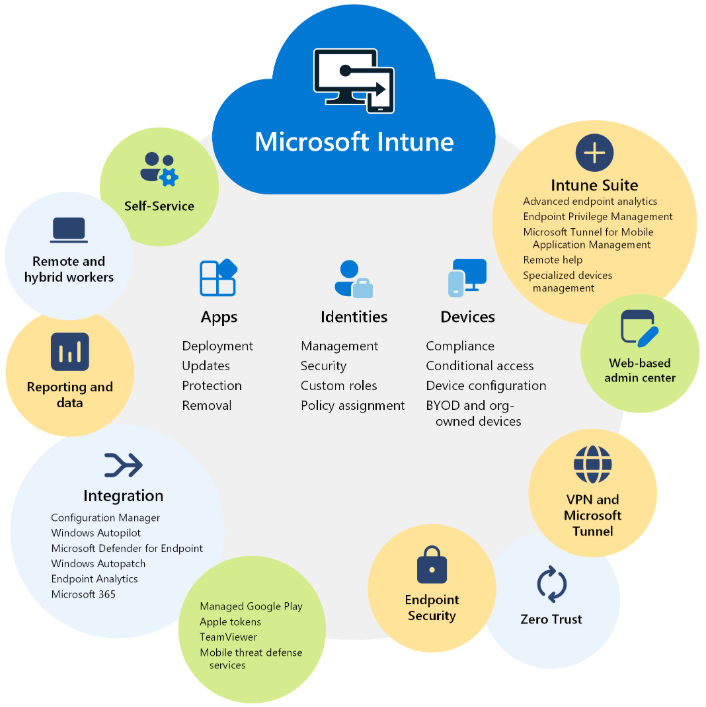
Setting up Microsoft Intune involves several steps to configure and manage devices, applications, and policies in your organization. Here’s a general outline of the process:
1. Create an Intune Subscription
- Sign up for Microsoft Intune through the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center.
- If you don’t have a Microsoft 365 subscription, you can sign up for one that includes Intune (e.g., Microsoft 365 E3 or E5).
- You can also try a trial version if you’re just exploring.
2. Set Up Azure Active Directory (Azure AD)
- Intune relies on Azure AD for device and user identity management.
- Make sure you have Azure AD set up, or create a new directory if necessary.
- Navigate to the Azure portal and ensure that your organization’s users and devices are synchronized with Azure AD.
3. Assign Licenses to Users
- Go to the Microsoft 365 admin center.
- Assign Intune licenses to the users who need to enroll their devices for management.
4. Configure Device Enrollment
- Mobile Device Management (MDM): In the Endpoint Manager admin center, go to Devices > Enroll devices and choose your platform (iOS, Android, Windows, etc.).
- You can configure automatic enrollment for Windows 10/11 devices or manually enroll mobile devices.
5. Set Up Enrollment Profiles (for Windows)
- For Windows 10/11, you can create an enrollment profile in Endpoint Manager.
- You can configure settings such as auto-enrollment, device restrictions, and security policies.
- For bulk enrollment, you may use Windows Autopilot.
6. Create Device Compliance Policies
- Go to Endpoint Manager > Devices > Compliance policies.
- Define the rules and settings for compliance, such as password requirements, encryption, and security features.
- Policies can be platform-specific (e.g., iOS, Android, Windows).
7. Configure Device Configuration Profiles
- Under Endpoint Manager, create configuration profiles to manage settings on enrolled devices.
- For example, configure Wi-Fi settings, VPN settings, email settings, etc.
- You can also deploy applications, manage updates, and enforce security configurations.
8. Set Up Application Management
- Go to Apps > All apps in the Endpoint Manager to add apps (Win32, iOS, Android, etc.).
- Configure deployment options, app policies, and permissions.
- For app protection, you can define policies for apps that are being used on personal devices or unenrolled devices.
9. Create Conditional Access Policies
- To enforce security requirements for users to access corporate resources, set up Conditional Access policies in Azure AD.
- You can require multi-factor authentication (MFA), device compliance, or location-based access controls.
10. Monitor and Report
- In the Endpoint Manager admin center, you can monitor device status, compliance, and user activities.
- Use reporting tools to track application deployment, policy compliance, and overall device health.
11. Test the Setup
- Enroll a test device to ensure that all settings, policies, and applications are applied as expected.
- Check if compliance policies are being enforced and if the conditional access works as intended.
Once the configuration is complete, Intune will manage your organization’s devices and apps, providing enhanced security and compliance monitoring.
Comments are closed